What is Amylose? Benefits, Structure, Function & Uses
What is amylose? Amylose is a type of starch found in many plants. It’s a linear polymer made up of glucose units joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds.
Let’s look at what it is, how it’s made, and what it’s used for.

Check out our new cookbook
Bitemybun's family recipes with complete meal planner and recipe guide.
Try it out for free with Kindle Unlimited:
Read for freeIn this post we'll cover:
- 1 Understanding Amylose: A Basic Guide
- 2 Amylose Content in Different Foods
- 2.1 How Does Amylose Content Impact Cooking?
- 2.2 What are the Nutritional Benefits of Amylose?
- 2.3 How Can Companies Use Amylose in Food Production?
- 2.4 What are Some Traditional Diets That Contain High Levels of Amylose?
- 2.5 How Can You Incorporate Foods High in Amylose into Your Everyday Diet?
- 2.6 What is the Best Way to Cook Foods High in Amylose?
- 3 Amylose Benefits
- 4 Structure
- 5 Function
- 6 Uses of Amylose – (C6H10O5)n
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions About Amylose
- 8 Conclusion
Understanding Amylose: A Basic Guide
Amylose is a type of polysaccharide, which means it is a complex carbohydrate composed of multiple sugar molecules bonded together. It is a linear molecule consisting of hundreds to thousands of glucose units linked by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. It is a component of starch, a common carbohydrate found in many foods, including cornstarch, rice, potatoes, and wheat.
How is Amylose Used in the Kitchen?
Amylose is a common ingredient in many recipes, particularly those that involve thickening or binding. Here are some ways that amylose can be used in the kitchen:
- Adding cornstarch to a sauce or soup to thicken it
- Using potato starch to bind ingredients in a recipe
- Adding rice flour to a batter to make it thicker
- Using arrowroot powder as a gluten-free thickener
What is the Relationship Between Amylose and Iodine?
One way to identify the presence of amylose in a food is to use iodine. When iodine is added to a food that contains amylose, it will turn a blue-black color. This is because iodine molecules can fit inside the helical structure of the amylose molecule, creating a complex that absorbs light and appears dark in color.
Amylose Content in Different Foods
Amylose is a type of starch found in plants that is made up of long chains of glucose units. It is a straight chain polymer, unlike amylopectin, which is highly branched. The amylose content in food impacts its cooking and nutritional properties.
How Does Amylose Content Impact Cooking?
The amylose content in food impacts its cooking properties in the following ways:
- Higher amylose content in rice makes it less sticky and easier to break apart when cooked.
- High amylose content in potatoes makes them firmer and more usable in making potato salads and other dishes that require the potatoes to maintain their shape.
- High amylose content in bread allows it to maintain its shape and texture when baked.
What are the Nutritional Benefits of Amylose?
Amylose has a few nutritional benefits, including:
- It is a type of resistant starch that can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- It can help with weight management because it is not broken down in the small intestine and can make you feel fuller for longer.
- It can help maintain healthy gut bacteria because it is broken down in the large intestine by bacteria.
How Can Companies Use Amylose in Food Production?
Companies can use amylose in food production in the following ways:
- It can be used as a binding agent in processed foods.
- It can be used to bring down the gel levels in food, making it less sticky and easier to handle.
- It can be used to produce resistant starch, which is a type of starch that is not broken down in the small intestine and can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
What are Some Traditional Diets That Contain High Levels of Amylose?
Some traditional diets that contain high levels of amylose include:
- The Japanese diet, which includes a lot of rice.
- The African diet, which includes a lot of beans and starchy vegetables.
- The Native American diet, which includes a lot of corn and potatoes.
How Can You Incorporate Foods High in Amylose into Your Everyday Diet?
You can incorporate foods high in amylose into your everyday diet in the following ways:
- Use black rice instead of white rice in your dishes.
- Include pinto beans in your salads and soups.
- Use sweet potatoes instead of white potatoes in your dishes.
- Choose bread made from whole grain flour instead of white flour.
- Include kidney beans in your chili and other dishes.
What is the Best Way to Cook Foods High in Amylose?
The best way to cook foods high in amylose is to:
- Cook rice in a large amount of water to bring down the gel levels and make it less sticky.
- Cook potatoes until they are just tender, then cool them down to maintain their shape.
- Soak beans overnight before cooking them to make them easier to digest.
Amylose Benefits
One of the key benefits of amylose is its ability to help with weight management. As a complex carbohydrate, amylose takes longer to digest, which means it keeps you feeling fuller for longer. This can help reduce overall calorie consumption and prevent overeating. Additionally, amylose is a low-energy starch, meaning it contains fewer calories per gram compared to other types of starch.
May Reduce the Risk of Diabetes
Amylose has been linked to a reduced risk of diabetes. This is because it is a resistant starch, which means it resists digestion in the small intestine and passes through to the large intestine. Here, it acts as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of healthy gut bacteria. This can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Supports Heart Health
Consuming amylose-rich foods has been associated with improved heart health. This is because amylose helps to lower cholesterol levels in the body. Additionally, it has been found to have a positive impact on blood pressure levels, which can further reduce the risk of heart disease.
May Help with Digestion
Amylose has a positive impact on digestion due to its prebiotic properties. It promotes the growth of healthy gut bacteria, which can improve overall digestive health. Additionally, amylose has been found to reduce the risk of colon cancer and kidney disease.
Provides a Balanced Source of Energy
Amylose is a complex carbohydrate that provides a balanced source of energy. Unlike simple sugars, which cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, amylose is digested slowly, providing a steady stream of energy throughout the day. This can help prevent energy crashes and keep you feeling alert and focused.
Found in Common Foods
Amylose is found in a variety of common foods, including:
- Rice (especially long-grain white rice)
- Potatoes (especially sweet potatoes and pinto potatoes)
- Beans
- Lentils
- Peas
- Leafy greens
- Whole grains
Easy to Incorporate into Your Diet
Incorporating amylose-rich foods into your diet is easy. Here are some tips:
- Start your day with a bowl of oatmeal or other whole grain cereal.
- Mix beans or lentils into soups, stews, and salads.
- Add leafy greens to sandwiches, wraps, and smoothies.
- Choose long-grain white rice instead of traditional white rice.
- Snack on raw vegetables, such as carrots and celery, with hummus or other bean dips.
Important Note
While amylose has many benefits, it is important to note that consuming large amounts of amylose-rich foods can have negative impacts. For example, consuming too much amylose can result in mold growth, especially in dry environments. Additionally, some people may be allergic to amylose or have difficulty digesting it. As with any dietary change, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet.
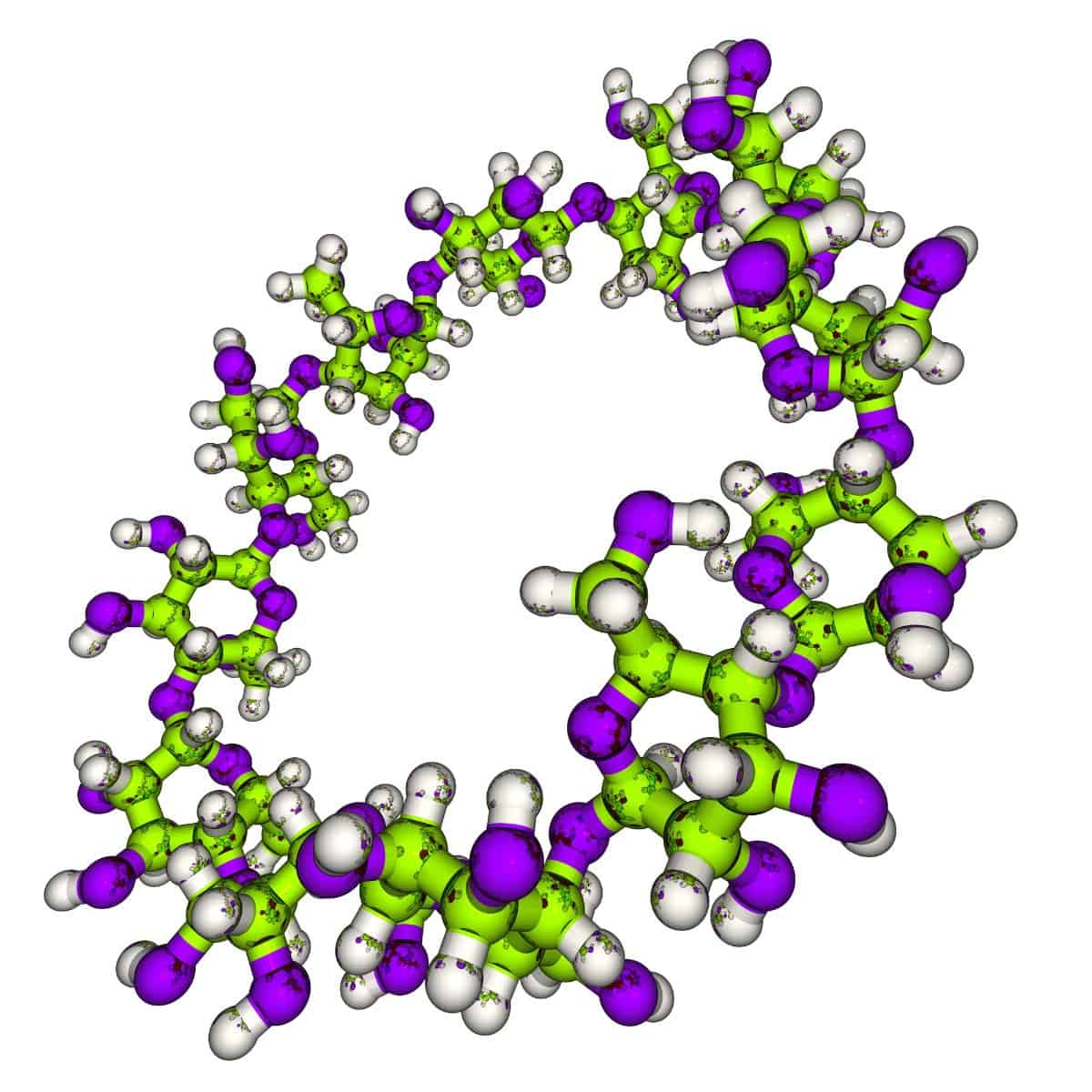
Structure
Amylose is a type of molecule that is made up of long chains of glucose units. Glucose is a type of sugar that is found in many different foods, and it is one of the main components of amylose. The glucose units in amylose are connected by covalent bonds, which means that they are held together by a shared pair of electrons. These bonds are known as glycosidic bonds.
The Different Types of Amylose Structures
There are two main types of amylose structures: straight chain and branched chain. Straight chain amylose is made up of a single chain of glucose units, while branched chain amylose has multiple chains that are connected to each other. The different structures of amylose can affect its properties and uses.
The Importance of Water in Amylose Structure
Water is an important component of amylose structure. The helical shape of amylose is stabilized by the presence of water molecules. Without water, the molecule would not be able to maintain its shape. This is why amylose is typically found in foods that contain a lot of water, such as fruits and vegetables.
The Role of Amylose in Starch Formation
Amylose is one of the two main components of starch, which is a type of carbohydrate that is used by plants to store energy. Starch is made up of both amylose and amylopectin, which is a branched chain molecule. Amylose helps to bind the starch molecules together, creating a structure that is able to store energy efficiently.
The Technical Details of Amylose Structure
For those who are interested in the technical details of amylose structure, here are a few key points to keep in mind:
- Amylose is made up of alpha glucose units, which means that the glucose molecules are oriented in a specific way.
- The glycosidic bonds between the glucose units are alpha-1,4 bonds, which means that the bond is formed between the first carbon atom and the fourth carbon atom in adjacent glucose units.
- The helix structure of amylose is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the glucose units.
- The resulting helix has a diameter of about 10 angstroms and a pitch of about 6 glucose units per turn.
- Amylose is amorphous, which means that it does not have a specific crystalline structure like some other molecules.
- Amylose can form intermediate structures between the straight chain and branched chain forms, depending on the conditions under which it is prepared.
In conclusion, the structure of amylose is highly complex and has numerous uses in food and other areas. Understanding the basic building blocks and helical structure of amylose is important for keeping foods fresh and for creating new products that rely on this molecule.
Function
Amylose, along with amylopectin, is a type of starch found in plants. It serves as a means of storing energy in the form of glucose molecules, which are produced through photosynthesis. Amylose is a long, straight chain of glucose units, compared to amylopectin, which is highly branched. This structure provides amylose with the ability to bind and store more water than amylopectin, making it a better source of energy.
Thickening and Binding Agent
Amylose is highly important in the process of making foods. It contains the potential to form a gel when heated, which aids in thickening and binding. This is particularly useful in making sauces, pie fillings, and other foods that require a solid, gel-like consistency. The gel is formed when amylose molecules bind together, forming a network of hydrogen bonds. This network traps water and other molecules, producing a thick, opaque substance.
Industrial Uses
Amylose has numerous industrial uses due to its ability to form a gel. It is commonly found in products such as paper coatings, adhesives, and films. The gel-forming ability of amylose also makes it an excellent emulsion stabilizer, which is important in the production of certain foods and cosmetics. Additionally, amylose is used in the production of biodegradable plastics.
Digestive Aid
Amylose is responsible for the helical structure of starch molecules, which is important in the digestive process. When we eat foods containing starch, enzymes break down the starch molecules into glucose units. The helical structure of amylose makes it more difficult for enzymes to break down, meaning it takes longer to digest. This slow digestion process provides a steady stream of glucose to the body, making it a good source of sustained energy.
Color and Film-Forming Agent
Amylose provides a white color to foods and is often present in foods that are prepared outside of the straight cooking process. It also has the potential to form a film, which is useful in food packaging. The film-forming ability of amylose is due to its hydrophobic nature, which allows it to concentrate at the surface of a liquid and form a solid film. This film provides a barrier to moisture and air, keeping the food fresh for a longer period of time.
Uses of Amylose – (C6H10O5)n
Amylose is a type of carbohydrate that is found in different forms in nature. It is a long chain of glucose molecules that is a main component of starch. In the previous sections, we have discussed the basic nature, structure, and function of amylose. Now, let’s dive into the different uses of amylose.
Food Industry
Amylose is an important compound in the food industry. It is found in high amounts in potatoes, sweet potatoes, and root vegetables. Some of the uses of amylose in the food industry include:
- Producing instant starches, which dissolve easily in water and are used as thickeners in cooking
- Making gum and binder for crisp coatings on French fries and other fried foods
- Providing a slow release of energy, as it is digested slowly and broken down into maltose
- Reducing the risk of chronic diseases by regulating digestion and stabilizing blood sugar levels
Textile, Film, Paper, and Pulp Industry
Amylose is also used in the textile, film, paper, and pulp industry. Some of its uses include:
- Producing permanent-press fabrics, as it helps to stabilize the fibers
- Making films and coatings, as it has good thermal conductivity and reduces the risk of copper testing
- Synthesis-related content, such as azo compounds and acidic radicals
- Analyzing colligative properties of solutions, such as salt and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Dietary Supplements
Amylose is also used in dietary supplements. Some of its uses include:
- Regulating digestion and reducing the risk of bowel disease
- Providing a slow release of energy, as it is digested slowly and broken down into maltose
- Stabilizing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of chronic diseases
Frequently Asked Questions About Amylose
Amylose consists of a single chain of glucose units connected by alpha glycoside linkages. These linkages create a straight chain, which is generally known as a polymer.
How is amylose compared to other biological compounds?
Amylose is a significant compound in starch particles, and it is generally compared to cellulose. Unlike cellulose, amylose contains alpha glycoside linkages that create a helical structure. This structure is firmly covered and spiral, making it more durable and resistant to digestion.
What are the sectors in which amylose is operative?
Amylose is utilized in a lot of sectors, including the cosmetic industry, water treatment, and food industry. It is also known for its pasting and resistant properties, making it an attractive compound for fixing blood sugar levels and decreasing the risk of germs.
What are the health advantages of amylose?
Amylose has several health advantages, including fixing blood sugar levels, decreasing the risk of germs, and promoting healthy digestion. Additionally, it is a polymer that is resistant to water, making it an attractive compound for utilization in the cosmetic industry.
How are the bonds formed in amylose?
The bonds in amylose are formed by alpha glycoside linkages, which connect the glucose units in a straight chain. These bonds are fixed and create a durable structure that is resistant to digestion.
What are the differences between amylose and amylopectin?
Amylose and amylopectin are two different models of starch. Amylose consists of a single chain of glucose units, while amylopectin consists of multiple chains of glucose units connected by alpha glycoside linkages. Additionally, amylose is generally known for its pasting and resistant properties, while amylopectin is known for its ability to create a gel-like structure.
Keeping these questions in mind, it is clear that amylose is a significant biological compound with several applications in different sectors. Its unique structure and durable bonds make it an attractive compound for utilization in various industries, including food, water treatment, and cosmetics. Additionally, its health advantages make it an attractive compound for promoting healthy digestion and fixing blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
The benefits of amylose are many, and it’s found in many of our favorite foods. It’s a great source of resistant starch, which helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels, and it can help you feel fuller longer. Amylose is a complex carbohydrate, and it’s a great ingredient to use in cooking.
Check out our new cookbook
Bitemybun's family recipes with complete meal planner and recipe guide.
Try it out for free with Kindle Unlimited:
Read for freeJoost Nusselder, the founder of Bite My Bun is a content marketer, dad and loves trying out new food with Japanese food at the heart of his passion, and together with his team he's been creating in-depth blog articles since 2016 to help loyal readers with recipes and cooking tips.
